The global electric vehicle (EV) industry has experienced exponential growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of the environmental benefits of electric vehicles. However, amidst this growth, the industry cannot seem to shake off its human rights abuse problem. From the mining of critical minerals to the manufacturing processes and supply chain management, numerous reports and investigations have shed light on the labor abuses and environmental degradation associated with the production of EV components.
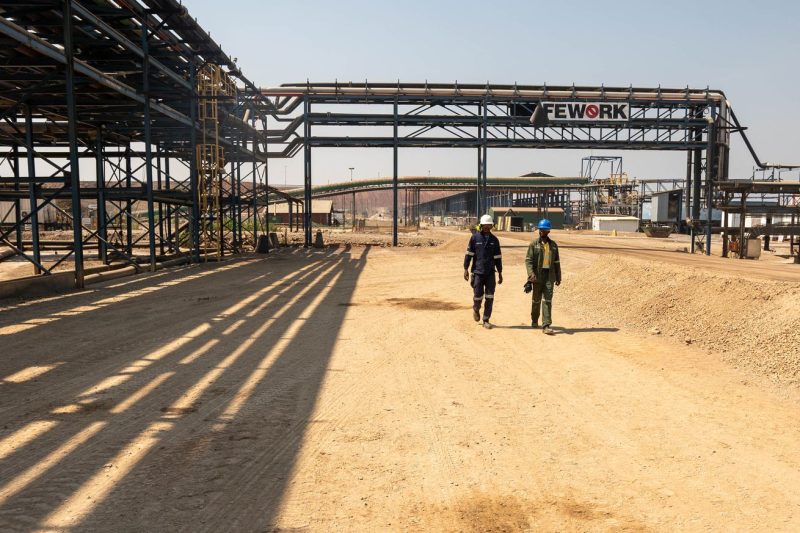
One of the key areas where human rights abuses are prevalent in the EV industry is in the mining of cobalt, a crucial component in lithium-ion batteries. Cobalt is mainly sourced from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), where child labor, hazardous working conditions, and human rights violations are widespread. Despite efforts by some companies to trace the source of their cobalt and ensure responsible sourcing, challenges remain in effectively monitoring and regulating the entire supply chain.
In addition to the sourcing of raw materials, the manufacturing processes in EV production facilities have also come under scrutiny for labor abuses. Reports of long working hours, low wages, lack of safety measures, and limited worker rights have been documented in some EV factories, particularly in countries where labor laws are less stringent. Companies must prioritize the well-being of their workers and ensure that fair labor practices are upheld throughout the manufacturing process.
Furthermore, the transportation and logistics aspects of the EV supply chain present their own set of challenges in terms of human rights abuses. Issues such as forced labor, exploitation of migrant workers, and lack of social protections for employees in the transportation sector have been reported in the context of EV production and distribution. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration among stakeholders across the supply chain to establish clear guidelines and standards for ethical practices.
To tackle the human rights abuse problem in the EV industry, concerted efforts are needed from governments, companies, and civil society organizations. Establishing transparent supply chains, conducting regular audits and inspections, implementing worker training programs, and enforcing strict labor standards are essential steps to improve the social sustainability of EV production. Companies should also engage with local communities, prioritize community development initiatives, and involve independent third parties to monitor and verify compliance with ethical standards.
In conclusion, while the electric vehicle industry holds great promise for reducing carbon emissions and mitigating climate change, it must address the persistent issue of human rights abuses in its supply chain. By committing to responsible sourcing, ethical manufacturing practices, and fair treatment of workers, the EV industry can strive towards a more sustainable and socially responsible future. It is crucial for stakeholders to work together towards creating a supply chain that not only delivers clean and efficient electric vehicles but also upholds the dignity and rights of all those involved in the production process.