Semiconductors are a vital component of the modern technology ecosystem, powering everything from smartphones to data centers. As the demand for smarter devices and faster computing continues to grow, it’s essential to understand how various semiconductor exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are performing in the market. In particular, we will delve into the comparison between two popular semiconductor ETFs: SMH and SOXX.
Semiconductor HOLDRs (SMH) and iShares PHLX Semiconductor ETF (SOXX) are both exchange-traded funds that focus on the semiconductor industry. However, there are distinct differences between the two that have played a significant role in their performance during various market conditions.
One key factor contributing to SMH’s resilience compared to SOXX is its diversified portfolio. SMH is known for holding a broader range of semiconductor stocks, which can help spread risk across the industry. This diversification provides a buffer against extreme volatility in individual stocks and allows SMH to remain relatively stable even in turbulent market conditions.
On the other hand, SOXX has a more concentrated portfolio, with a heavier emphasis on specific semiconductor companies. While this focused approach can lead to higher returns during bullish market phases, it also exposes SOXX to more significant risks if any of its key holdings underperform.
Moreover, the weighting methodology of the two ETFs differs significantly. SMH follows a capped-capitalization-weighted approach, which means that individual holdings cannot exceed a certain percentage of the total portfolio. This prevents any single stock from dominating the ETF’s performance, contributing to its overall stability.
In contrast, SOXX utilizes a market-cap-weighted methodology, where stocks with larger market capitalizations have a more substantial impact on the ETF’s performance. While this approach can lead to outperformance if mega-cap semiconductor stocks do well, it can also amplify losses if these stocks face challenges.
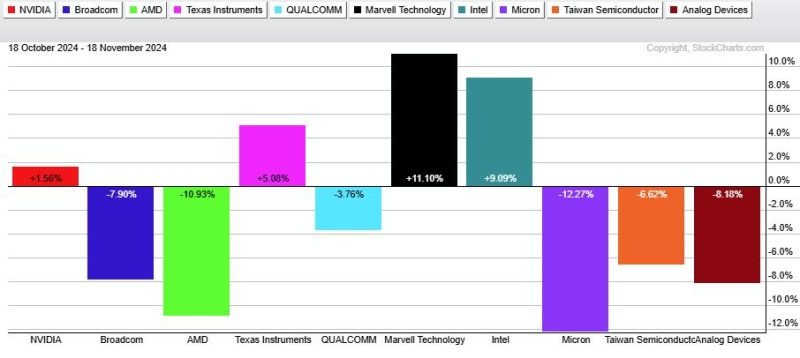
Additionally, the sector dynamics and performance of specific semiconductor companies can influence the relative performance of SMH and SOXX. Changes in consumer demand, technological advancements, and global trade issues can all impact semiconductor stocks differently, leading to variations in the two ETFs’ performance.
In conclusion, when comparing SMH and SOXX, it’s essential to consider factors such as portfolio diversification, weighting methodology, and sector dynamics. While SMH’s diversified approach and capped-capitalization weighting have contributed to its stability, SOXX’s concentrated portfolio and market-cap weighting make it more susceptible to volatility. Understanding these differences can help investors make informed decisions when choosing a semiconductor ETF that aligns with their investment goals and risk tolerance.