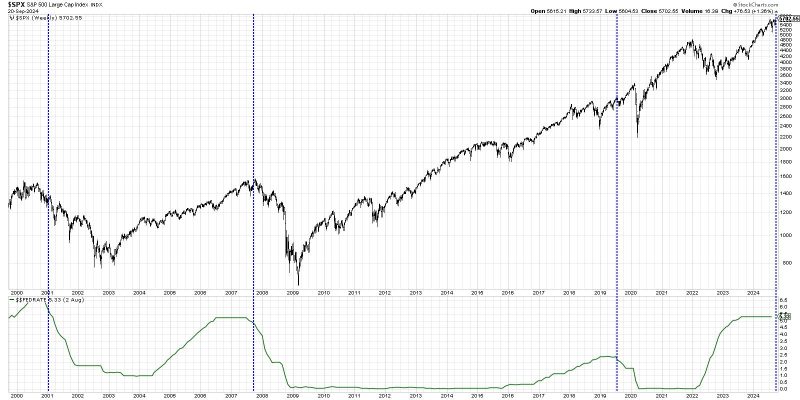
In the world of finance, the decision to cut interest rates is a crucial one that can have a ripple effect on various aspects of the economy. One key area that is often greatly impacted by rate cuts is the stock market. Investors are constantly speculating about whether rate cuts will send stocks soaring or plummeting, leading to a great deal of debate over the relationship between rate cuts and stock performance.
Historically, rate cuts have often been seen as a boon for the stock market. When interest rates are cut, borrowing becomes cheaper, making it easier for businesses to invest and grow. This can be particularly beneficial for industries such as housing and construction, which rely heavily on borrowing to finance projects. Lower interest rates can also lead to increased consumer spending, as people are more likely to take out loans for big-ticket items like homes and cars.
However, the impact of rate cuts on the stock market is not always straightforward. In some cases, rate cuts can actually signal underlying weaknesses in the economy, prompting investors to sell off stocks in favor of safer investments. Additionally, if rate cuts are perceived as a desperate measure by central banks to prop up a struggling economy, it can lead to uncertainty and volatility in the stock market.
Another factor to consider is the timing of rate cuts in relation to stock performance. While rate cuts can provide a short-term boost to stock prices, the long-term effects may be more muted. Investors may start to question the sustainability of the gains fueled by rate cuts, leading to a correction in stock prices.
Ultimately, the relationship between rate cuts and stock performance is complex and multifaceted. While rate cuts can provide a temporary lift to the stock market, the broader economic context and market sentiment play a significant role in determining the long-term impact on stock prices. Investors should carefully consider all these factors before making investment decisions based on rate cuts alone.